Vision-based reinforcement learning can benefit from object-centric scene representation, which factorizes the visual observation into individual objects and their attributes, such as color, shape, size, and position. While such object-centric representations can extract components that generalize well for various multi-object manipulation tasks, they are prone to issues with occlusions and 3D ambiguity of object properties due to their reliance on single-view 2D image features. Furthermore, the entanglement between object configurations and camera poses complicates the object-centric disentanglement in 3D, leading to poor 3D reasoning by the agent in vision-based reinforcement learning applications. To address the lack of 3D awareness and the object-camera entanglement problem, we propose an enhanced 3D object-centric representation that utilizes multi-view 3D features and enforces more explicit 3D-aware disentanglement. The enhancement is based on the integration of the recent success of multi-view Transformer and the prototypical representation learning among the object-centric representations. The representation, therefore, can stably identify proxies of 3D positions of individual objects along with their semantic and physical properties, exhibiting excellent interpretability and controllability. Then, our proposed block transformer policy effectively performs novel tasks by assembling desired properties adaptive to the new goal states, even when provided with unseen viewpoints at test time. We demonstrate that our 3D-aware block representation is scalable to compose diverse novel scenes and enjoys superior performance in out-of-distribution tasks with multi-object manipulations under both seen and unseen viewpoints compared to existing methods.
We compare novel view synthesis and per-slot reconstructions on Clevr3D and IsaacGym3D. Compared to OSRT, our method maintains comparable novel view synthesis quality while producing cleaner and more coherent slot decompositions.
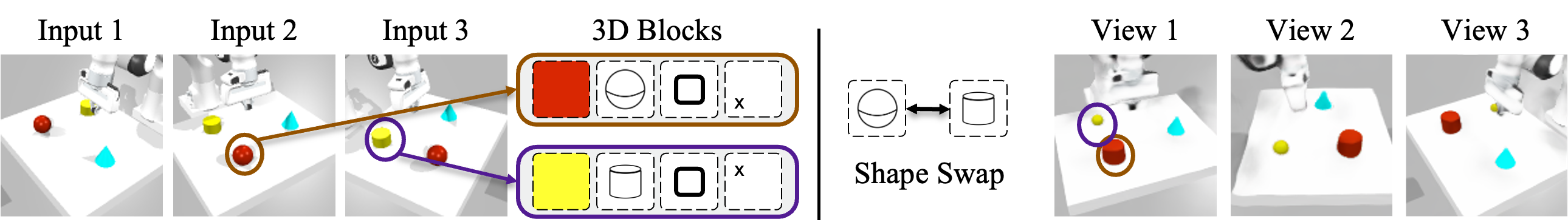
We swap object blocks within a scene and synthesize novel views on Clevr3D and IsaacGym3D. While the top row shows standard novel view synthesis, the bottom row shows results after swapping object properties (shape, size, color, position), demonstrating controllable and disentangled 3D object representations.
Goal image
Success episode

Goal image

Success episode

Goal image

Success episode

Goal image

Success episode

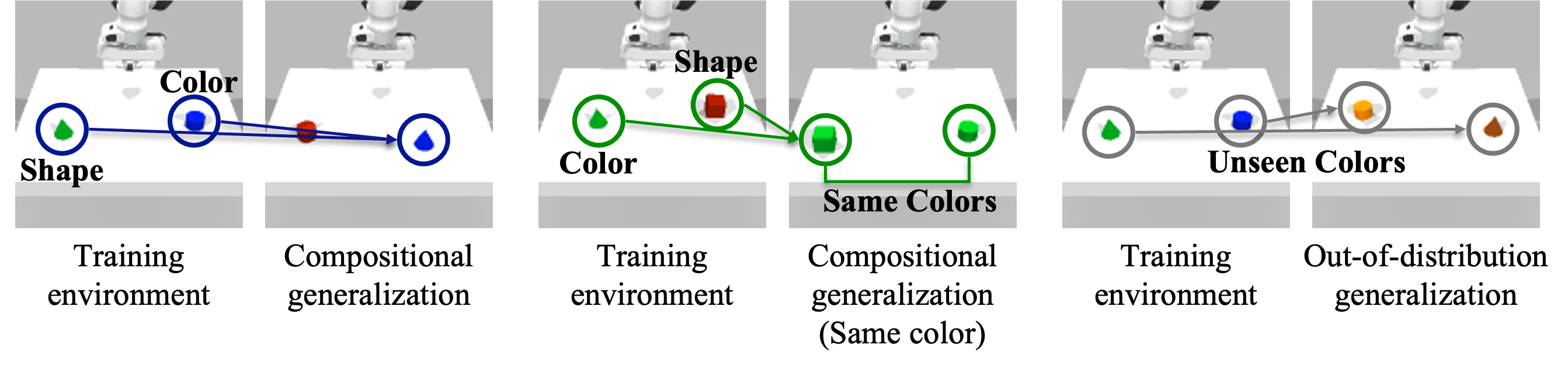
We evaluate generalization over four settings: in-distribution scenes, compositional generalization with novel object combinations, same-color compositional generalization, and out-of-distribution scenes containing unseen properties. Across all settings, our model consistently rolls out successful episodes, demonstrating robust generalization beyond the training distribution.